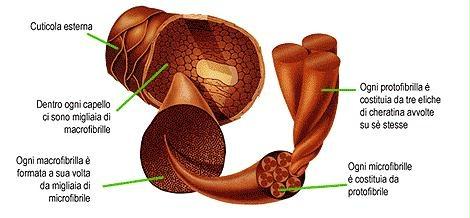
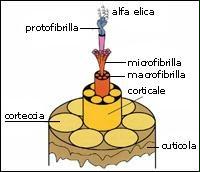
In addition to water, the elements that compose the chemical composition of hair are: keratin, lipids, minerals and pigments.
Keratin is a protein found in the cortex. Keratin is composed of 18 amino acids. The most abundant amino acids are: Cysteine, cystine, serine, glutamic acid, glycine, threonine, arginine, valine, leucine and isoleucine.
Alpha keratin, fibrous and with a low sulphur content, is the protein we find in the greatest quantity in hair. It has a molecular weight of around 45,000 and is insoluble in water. Keratin may be deformed with water vapor (“styling”).
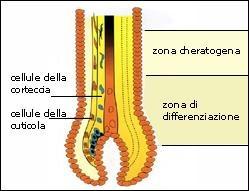
The hair keratinization process is regulated by various elements (hormones, vitamins, genetic factors and metabolism) and is connected to the metabolism of cholesterol and its esterification with fatty acids synthesized by the epidermis. Dietary deficiencies and/or enzyme defects due to cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis may lead to irregular keratinization which results in structural defects in the hair shaft.
Lipids present in the hair’s chemical structure are made up of triglycerides, waxes, phospholipids, cholesterol, squalene and free fatty acids. Quantifying these is extremely complex given that they are mostly derived from sebum.
Minerals and trace elements of the hair’s chemical structure are an essential component of the protein-enzymatic systems. These are iron, magnesium, zinc, copper and lead.
Protein and/or electrolyte deficiencies in the hair’s chemical structure may create hair problems and will become evident under the microscope due to the presence of a thin shaft associated with small bulbs. If the hair is structurally thin the bulbs will instead appear to be a normal size.
The pigments consist of melanin (colored substances), present in the hair in a diffused or granular form. These are not water soluble but they are soluble in strong acids and the color may be removed with hydrogen peroxide.
Melanocytes, using tyrosine (an amino acid that synthesizes protein) as a precursor, synthesize two main types of melanin: eumelanin, dark and present in black hair, and pheomelanin, lighter and present in golden, blonde and red hair.
The main chemical elements present in hair are composed of carbon (45%), oxygen (28%), nitrogen (15%), hydrogen (6.7%) and sulphur (5.3%).
Moreover, various trace elements are present (these can be found by performing a trace mineral analysis): Ca, Mg, Sr, B, Al, Si, Na, K, Zn, Cu, Mn, Fe, Ag, Au, Hg, As,Pb, Sd, Ti, W, Mo, I, P, Se. It is important to remember that the percentages of trace elements present in hair are subjective and vary in each individual.
Cystine is the main amino acid present in keratin (17.5%), followed by serine (11.7%) and glutamic acid (11.1%). Threonine, arginine and glycine are instead present in smaller percentages (approximately 6%).
80% of the weight of hair is due to the presence of protein (amino acid polymers), among which the main one is keratin, composed of 18 amino acids.
The main amino acids that make up keratin are: cystine (17.5%), serine (11.7%) glutamic acid (11.1%), threonine (6.9%), glycine (6.5%) and lastly arginine (5.6%).

 Italiano
Italiano  Português
Português  Français
Français  Español
Español